Confidence intervals (CIs) are a vital component of statistical analysis, especially in medical research. They provide a range of values that help researchers determine the reliability and precision of study results. In 2024, as medical research continues to evolve with advancements in technology and data collection, the importance of confidence intervals has become even more significant. This article will explore why confidence intervals are crucial for medical research, how they contribute to more accurate interpretations, and why they are indispensable for evidence-based medicine today.
What Are Confidence Intervals?
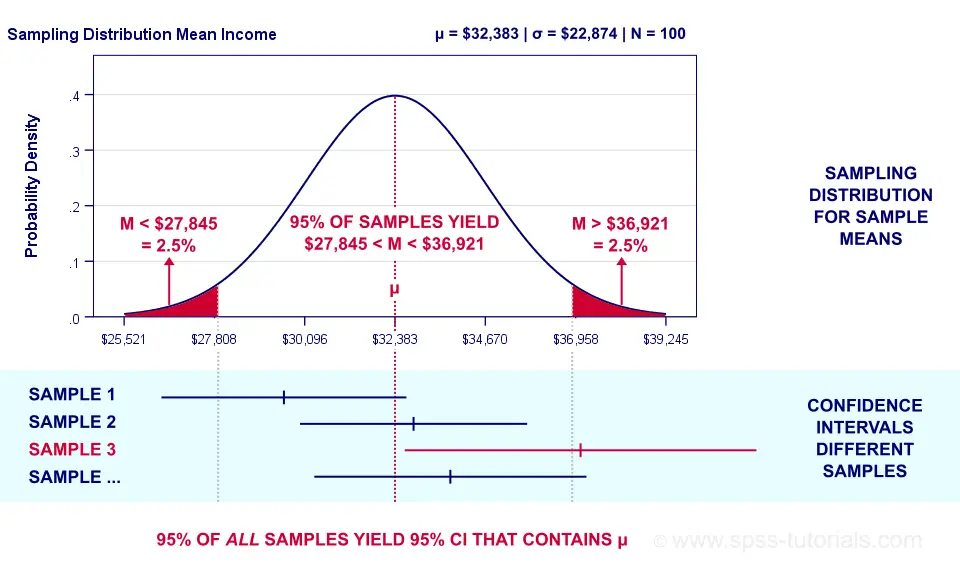
A confidence interval is a range of values, derived from sample data, that is likely to contain the true population parameter with a certain level of confidence. For instance, a 95% confidence interval implies that if the same study were repeated multiple times, 95% of the intervals generated would contain the true value of the parameter being measured.
In medical research, confidence intervals are typically used to estimate the effect of a treatment, a disease prevalence rate, or any other critical variable. Unlike p-values, which only tell whether an effect exists, confidence intervals provide information about the possible size of the effect and its variability.
Why Are Confidence Intervals Important in Medical Research?
1. Precision in Estimates
Medical research often deals with estimates that come from sample populations. These samples are meant to reflect the broader population. Confidence intervals offer a measure of precision. The narrower the interval, the more precise the estimate. This precision is crucial when determining the effectiveness of new treatments or the prevalence of diseases.
In 2024, as research becomes more reliant on big data and machine learning, the ability to compute highly precise confidence intervals will enhance the overall reliability of medical studies.
2. Interpreting Clinical Significance
Statistical significance, commonly measured by p-values, is not the only factor researchers should consider. Confidence intervals also play a critical role in determining clinical significance, which refers to the practical importance of a research finding in a clinical setting. A study might show that a drug has a statistically significant effect on reducing symptoms, but if the confidence interval for that effect is very wide, it may indicate that the drug’s actual effectiveness could vary dramatically in practice.
For example, a confidence interval for a treatment’s effectiveness might range from a 2% to a 25% improvement in outcomes. While the result may be statistically significant, such a wide range could make the treatment’s actual utility in a clinical setting uncertain. By narrowing the confidence intervals, researchers can provide more actionable insights for clinicians and patients alike.
3. Avoiding Overreliance on P-Values
One of the major criticisms of traditional hypothesis testing in medical research is the overreliance on p-values. While p-values can indicate whether a result is statistically significant, they do not provide information about the magnitude or precision of the effect. Confidence intervals, on the other hand, give a more comprehensive view, allowing researchers to make more informed decisions about the results.
In 2024, medical research is increasingly moving away from an overemphasis on p-values alone. Confidence intervals offer a more nuanced understanding, helping to prevent misleading conclusions that may arise from focusing solely on whether or not a p-value is below a certain threshold.
The Role of Confidence Intervals in Evidence-Based Medicine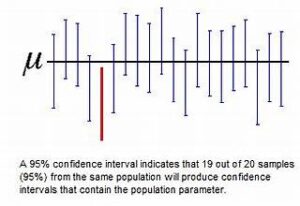
1. Improved Decision-Making
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) relies on the integration of the best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values. Confidence intervals provide a range of values that can help clinicians make better decisions based on the most likely outcomes. By understanding the potential range of treatment effects, clinicians can better weigh the benefits and risks of a particular intervention.
For instance, in assessing the effectiveness of a new drug, a clinician might be more cautious if the confidence interval suggests the treatment effect could be minimal or nonexistent in some patients, even if the average effect is positive.
2. Enhanced Transparency in Reporting
In recent years, there has been a growing push for transparency in medical research reporting. Confidence intervals play a vital role in this effort by offering a clear, interpretable range of potential outcomes. This transparency is particularly important in the publication of clinical trials, where decisions about treatment efficacy can have life-altering consequences.
In 2024, medical journals and research institutions are increasingly requiring the reporting of confidence intervals alongside p-values. This shift toward transparency helps ensure that research findings are presented in a way that fully reflects the uncertainty inherent in any study.
The Future of Confidence Intervals in Medical Research
1. Big Data and Machine Learning
As the volume of data available for medical research continues to grow, so too does the complexity of statistical analyses. Confidence intervals will remain essential for summarizing the results of big data analyses, helping to communicate the uncertainty associated with massive datasets.
Machine learning models, which are increasingly used to predict outcomes in medicine, also benefit from confidence intervals. These intervals can help quantify the uncertainty in model predictions, giving researchers and clinicians a better understanding of the reliability of these predictions.
2. Adaptive Clinical Trials
Adaptive clinical trials, which allow for modifications to the trial procedure based on interim results, are becoming more common. Confidence intervals are particularly useful in these settings because they allow researchers to assess whether the observed effects are sufficiently precise to justify continuing, modifying, or stopping the trial early.
In 2024, adaptive trials are expected to become a standard in medical research, especially in the development of personalized medicine and targeted therapies. Confidence intervals will be an indispensable tool in ensuring the validity and reliability of these trials.
Common Misinterpretations of Confidence Intervals
Despite their importance, confidence intervals are often misunderstood. One common mistake is to interpret a 95% confidence interval as meaning that there is a 95% probability that the true parameter lies within the interval. In reality, the interval either contains the true value, or it does not; the 95% refers to the long-run probability that similar intervals would contain the true value if the experiment were repeated many times.
Another misconception is that wider confidence intervals necessarily indicate more uncertainty. While wider intervals do suggest more variability in the estimate, they can also result from smaller sample sizes or less efficient study designs. In 2024, as medical research continues to evolve, it is critical that researchers and clinicians are educated on the proper interpretation and use of confidence intervals.
Conclusion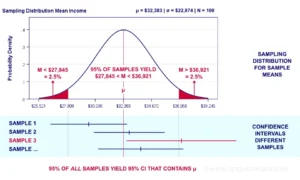
Confidence intervals are an indispensable tool in modern medical research, offering insights into the precision and reliability of study results. In 2024, their importance has only grown as the medical field shifts toward more complex data analyses, adaptive trial designs, and evidence-based practices. By providing a range of possible outcomes, confidence intervals help researchers, clinicians, and policymakers make more informed decisions that ultimately lead to better patient care and more effective medical interventions.